Table of Content
Introduction to Porter Five Forces Model
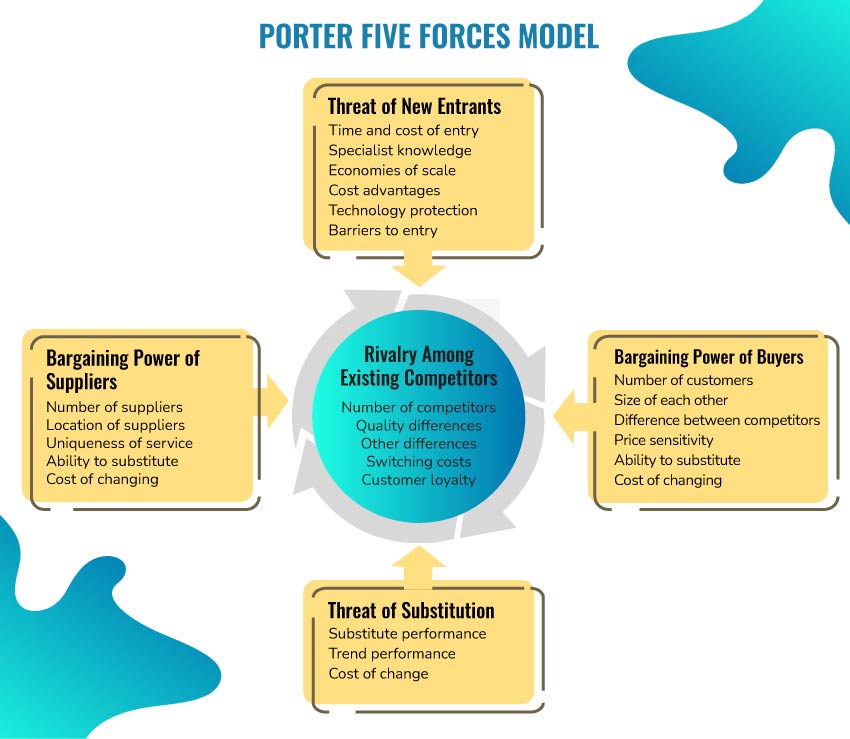
Porter’s Five Forces Model is an important competitive analysis model given by Michael Porter in 1979 as a model to assess and evaluate the competitive strength and position of the organization. The Five Forces that are examined in this model include the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products, the bargaining power of customers, rivalry among the existing firms, and the bargaining power of suppliers.
The need for Porter Five Forces Model
The use of the Porter Five Forces Model helps to analyze the competitive strength and position of the organization. The Porter Five Forces analysis can be undertaken by the organization for strategic planning as the use of this model helps to evaluate the industry attractiveness and investment options. By using this model, the organizations can also plan different strategies to remain successful in the industry by considering the competitive factors impacting the operations of the organization.
How to apply Porter’s Five Forces model?
The model devolves on the two schools of thought i.e. doing what the other firms in the industry are doing but at the cheaper rate and doing something that nobody is doing. The Porter Five Forces Model can be used in the manner discussed as follows-
Rivalry among the existing firms-
This force can be evaluated by the organization by considering the number of direct and indirect competitors in the industry. The factors that need to be considered while evaluating this force are listed as follows-
- What is the level of competition in the industry?
- Who are the direct competitors?
- Who are the indirect competitors?
- What do organizations do to remain competitive in the industry?
The threat of substitute products
The threat of substitute products is the possibility that the customers can find a different alternative to the organization’s products. The threat of substitute products can be evaluated by considering the following questions-
- How easy is it for the customers to find alternatives to the organization's products and services?
- How many substitute products or services are available in the market?
- What is the switching cost of the substitute products?
Bargaining power of buyers
The bargaining power of buyers is assessed by the business firm by evaluating the number of buyers in the market, the importance of each buyer, size of the products or services bought by each buyer, switching cost of buyers, etc. Thus, the key questions that are considered while determining the bargaining power of the buyers are discussed as follows-
- How many buyers are there in the market?
- What is the size of each buyer?
- What is the power of each buyer?
Bargaining power of suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is assessed by the organization to assess how easily suppliers can increase their prices. The bargaining power of suppliers can be determined by considering a few questions in mind which are listed as follows-
- How many suppliers are there?
- Is the product or service that the suppliers provide unique?
- How many alternative suppliers are there in the market?
- How expensive is it for the organization to switch to other suppliers?
The threat of new entrants-
The organization can also assess the threat of new entrants in the market by considering how easily the new firms can enter the market and threaten the competitive position of the organization. The key questions that can be considered while determining the threat of new entrants are listed as follows-
- How much capital is needed to start the new venture?
- What are the barriers to the entry of new firms?
- What rules and regulations restrict the entry of new firms into the industry?
- How easy is it for the new firm to enter the market?
Porter Five Forces Model real example
To understand the application of this planning model, let us delve deep into Woolworths Porter Five Forces Model.
| Porter Five Forces | Level | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Bargaining power of buyers | Medium | The bargaining power of Woolworths is moderate as, despite the presence of a large number of companies in the retail sector and higher competition from Coles and Aldi, the product differentiation raises the switching cost of the buyers. In addition to this, Woolworths offers low-priced products to the customers which also reduces the buyers’ bargaining power. |
| The threat of new entrants | High | The threat of new entrants is high in industry as setting up a retail business requires large amounts of capital and the existing firms like Woolworths have established strong economies of scale with years of experience. Moreover, higher government regulations in food safety and licensing also reduce the threat of new entrants in the industry. Not just this, the presence of various dominating firms such as Woolworths, Coles, Aldi, etc. also reduces the threat of new entrants in the industry. The existing firms have access to established channels of distribution, strong supplier relations, etc. which increases the risk of new firms losing their investment. |
| Bargaining power of suppliers | Medium | The bargaining power of suppliers is moderate as Woolworths faces higher bargaining power of suppliers for certain products such as Campos Organic coffee beans as there are limited Certified Organic farms and suppliers of this product. In contrast to this, the bargaining power of suppliers is low for raw materials available by a large number of suppliers in the retail sector. In addition to this, Woolworths also has limited dependence on the suppliers for various products which also reduces the bargaining power of the suppliers. |
| The threat of substitute products | Moderate | The threat of substitute products of Woolworths is moderate due to the presence of a large number of competitors but higher product differentiation and quality of Woolworths products. |
| Rivalry among existing firms | High | Woolworths faces tough competition from various firms such as Aldi, Coles, Amazon, Tesco, etc. Woolworths has attained a 37 % share in the grocery sector in Australia but due to lower switching costs and lack of differentiation in the retail products, there is higher rivalry among the existing firms |